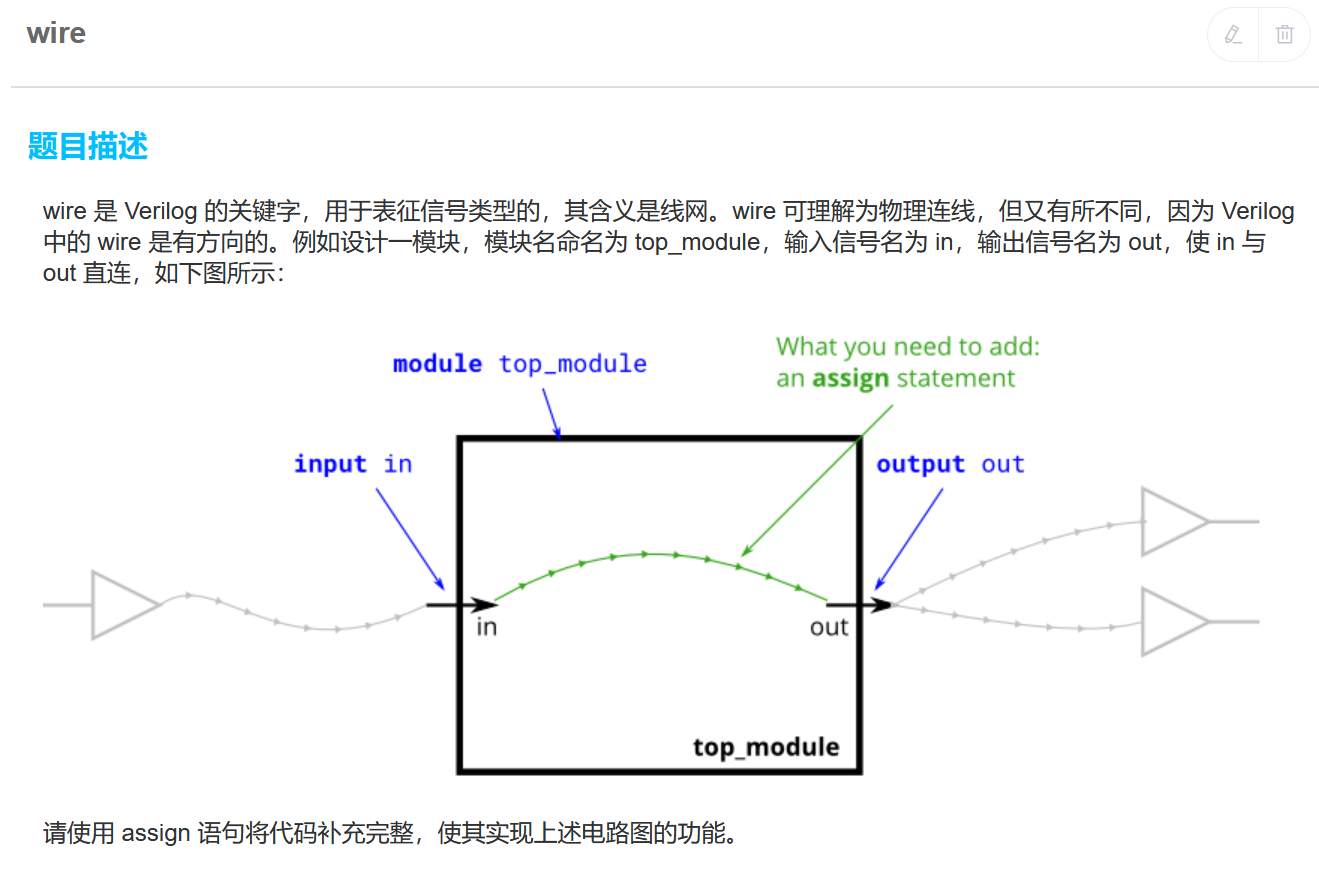
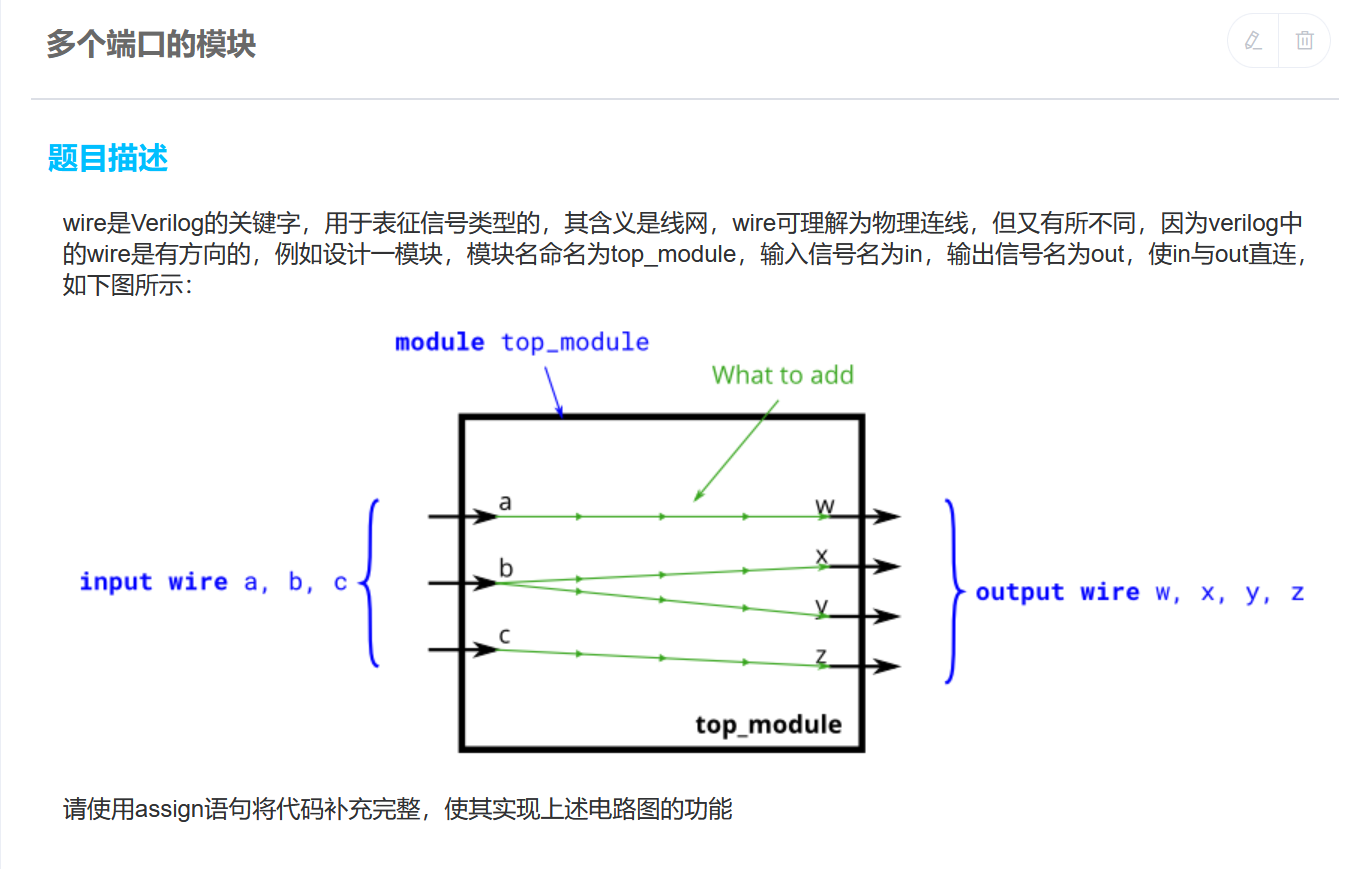
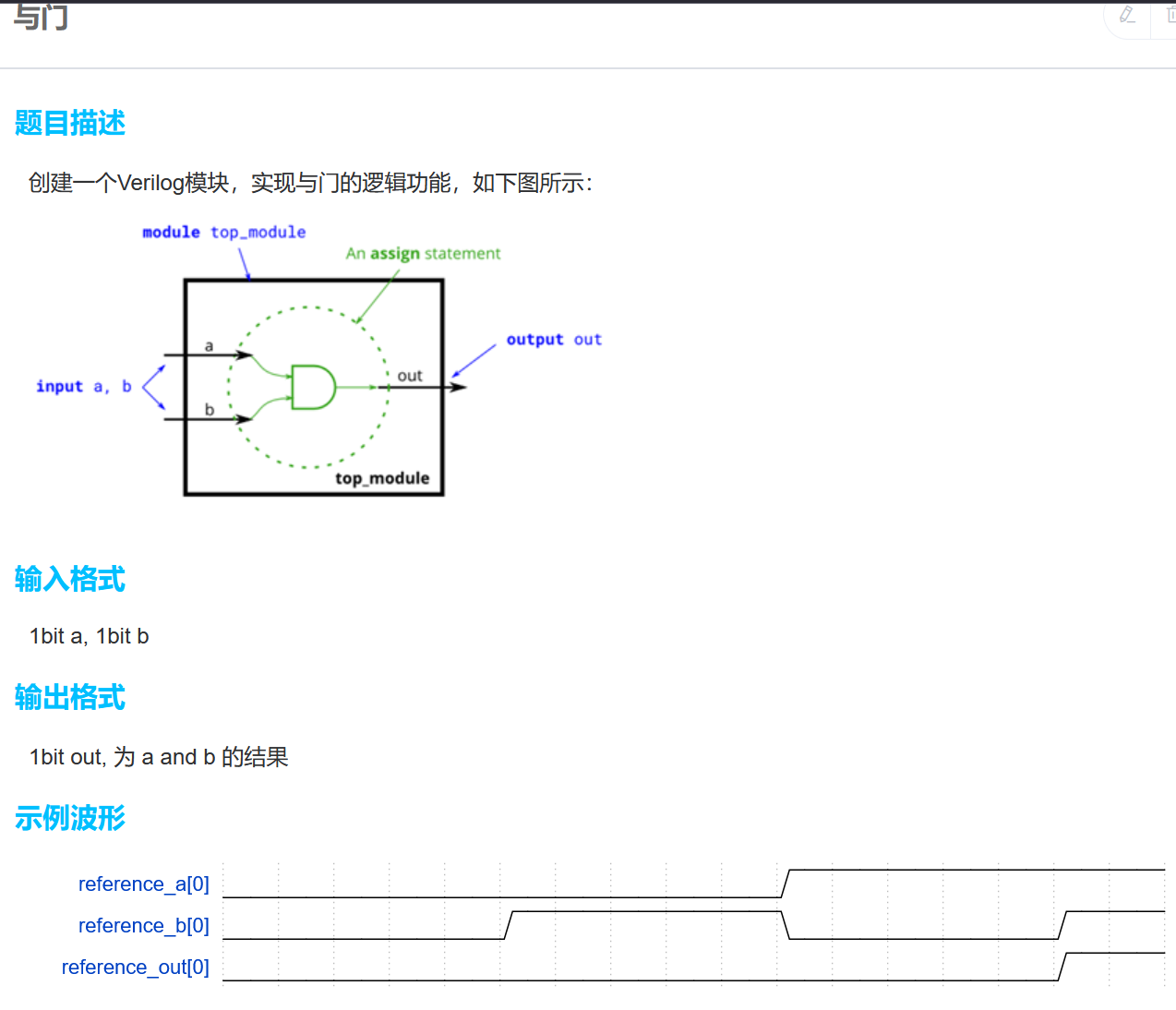
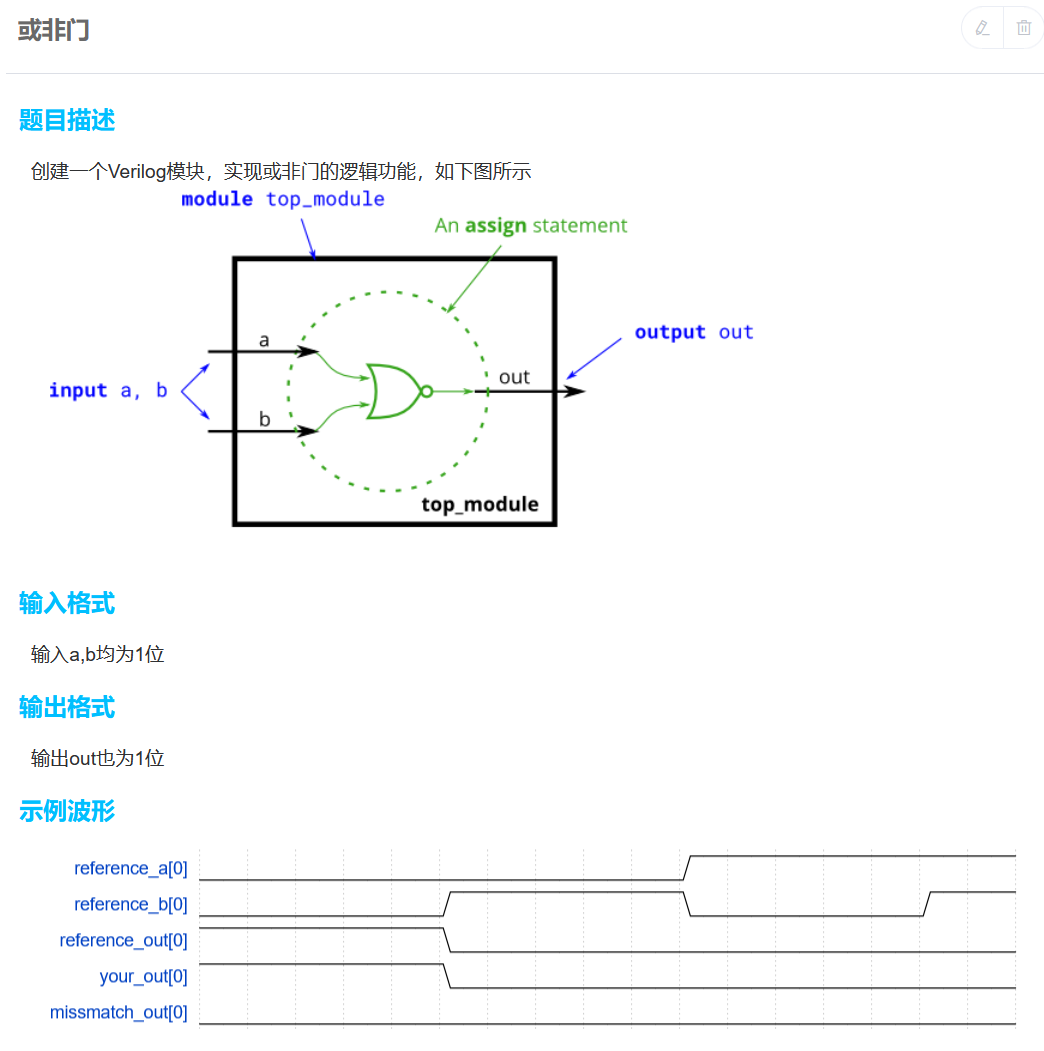
数列求和

PC r0 r1 r2 r3
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0) # 初始状态
(1, 10, 0, 0, 0) # 执行PC为0的指令后, r0更新为10, PC更新为下一条指令的位置
(2, 10, 0, 0, 0) # 执行PC为1的指令后, r1更新为0, PC更新为下一条指令的位置
(3, 10, 0, 0, 0) # 执行PC为2的指令后, r2更新为0, PC更新为下一条指令的位置
(4, 10, 0, 0, 1) # 执行PC为3的指令后, r3更新为1, PC更新为下一条指令的位置
(5, 10, 1, 0, 1) # 执行PC为4的指令后, r1更新为r1+r3, PC更新为下一条指令的位置
(6, 10, 1, 1, 1) # 执行PC为5的指令后, r2更新为r2+r1, PC更新为下一条指令的位置
(4, 10, 1, 1, 1) # 执行PC为6的指令后, 因r1不等于r0, 故PC更新为4
(5, 10, 2, 1, 1) # 执行PC为4的指令后, r1更新为r1+r3, PC更新为下一条指令的位置
(6, 10, 2, 3, 1)
(4, 10, 2, 3, 1)
(5, 10, 3, 3, 1)
(6, 10, 3, 6, 1)
(4, 10, 3, 6, 1)
(5, 10, 4, 6, 1)
(6, 10, 4, 10, 1)
(4, 10, 4, 10, 1)
(5, 10, 5, 10, 1)
(6, 10, 5, 15, 1)
(4, 10, 5, 15, 1)
(5, 10, 6, 15, 1)
(6, 10, 6, 21, 1)
(4, 10, 6, 21, 1)
(5, 10, 7, 21, 1)
(6, 10, 7, 28, 1)
(4, 10, 7, 28, 1)
(5, 10, 8, 28, 1)
(6, 10, 8, 36, 1)
(4, 10, 8, 36, 1)
(5, 10, 9, 36, 1)
(6, 10, 9, 45, 1)
(4, 10, 9, 45, 1)
(5, 10, 10, 45, 1)
(6, 10, 10, 55, 1)
(7, 10, 10, 55, 1)
(7, 10, 10, 55, 1)
(7, 10, 10, 55, 1)
...
执行到最后 处理器处于一个死循环,不断执行指令七的状态,数列求和的结果存在r2。r0用来存储循环次数,r1用于计数,r2用于存放数列求和的结果,r3用于存放计数时的步进。
计算10以内奇数之和

li r0,11 #0
li r1,1 #1
li r2,0 #2
li r3,2 #3
add r2,r2,r1 #4
add r1,r1,r3 #5
bner0 r1,4 #6
bner0 r3,7 #7
验证
PC r0 r1 r2 r3
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
(1, 11, 0, 0, 0)
(2, 11, 1, 0, 0)
(3, 11, 1, 0, 0)
(4, 11, 1, 0, 2)
(5, 11, 1, 1, 2)
(6, 11, 3, 1, 2)
(4, 11, 3, 1, 2)
(5, 11, 3, 4, 2)
(6, 11, 5, 4, 2)
(4, 11, 5, 4, 2)
(5, 11, 5, 9, 2)
(6, 11, 7, 9, 2)
(4, 11, 7, 9, 2)
(5, 11, 7, 16, 2)
(6, 11, 9, 16, 2)
(4, 11, 9, 16, 2)
(5, 11, 9, 25, 2)
(6, 11, 11, 25, 2)
(7, 11, 11, 25, 2)
(7, 11, 11, 25, 2)
(7, 11, 11, 25, 2)
...
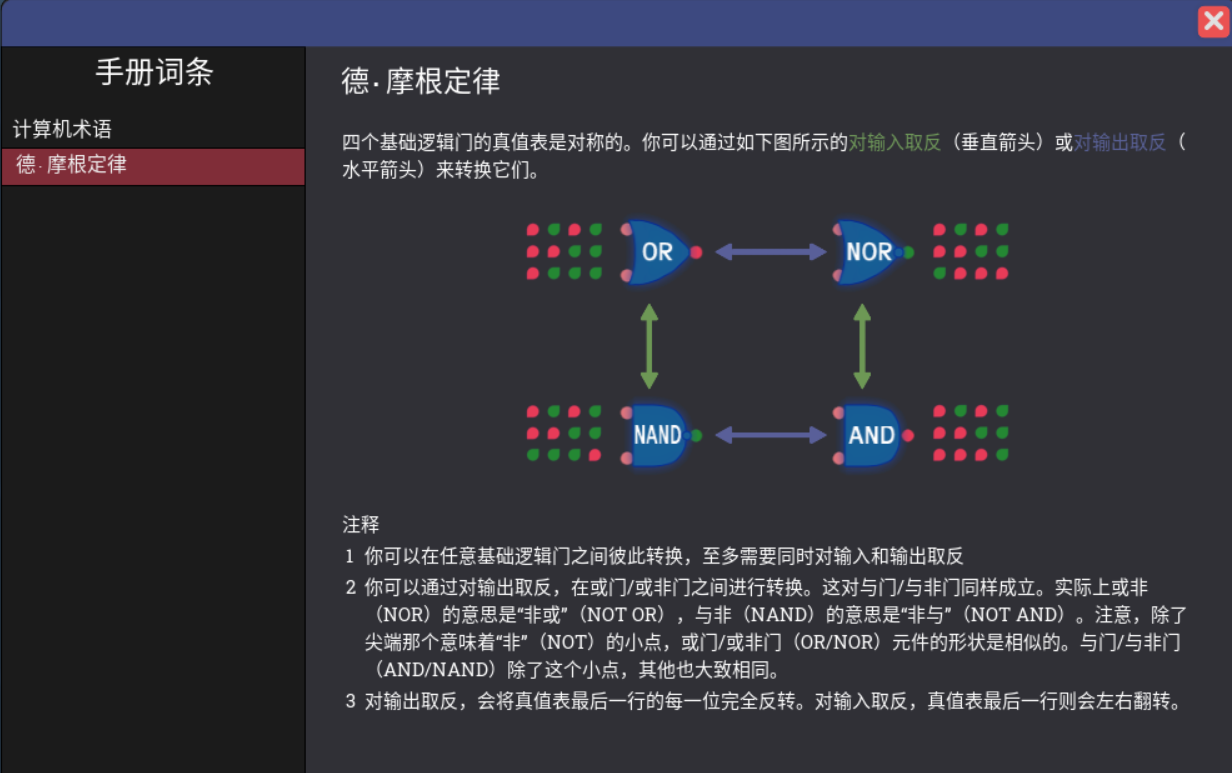
指令集架构的状态机模型
状态机的定义

状态集合是指isa中定义的存储器件所有可能的状态
激励事件集合是指 状态和状态之间的转换因什么而发生,这些事件的集合
状态转移规则 则是指从某种状态到某种状态之间具体做了什么事情
在ISA中,寄存器和内存就是存储状态的器件,激励事件是执行指令,状态转移规则是指指令的语义
sisa的状态机模型为

状态机视角下的C数列求和程序